
Mission for Global Change
Roadmap to Prevent Wars and Secure Global Rights for the People of Earth
1. Purpose: To Prevent Wars and Secure Global Rights for the People of Earth.
2. Definitions:
Global: ‘Global’ is referred to something related to the interconnected world. The world ‘Global’ is used to communicate the ‘world Level’ or the ‘entire earth level’.
Global Problems: Human challenges like war, international corruption, crime, terrorism and poverty, unemployment, malnutrition, illiteracy, illness and other export driven problems of the people that require a collective global endeavor are referred to as ‘Global Problems’,
Global Rights: The rights of the people of the earth necessary to address the above said Global Problems, granted by the constitution of a global agency like world government, and the same can be protected by the right of filing writ petition in local bench of global court is termed ‘Global Rights of people of earth’. Global Rights are also called the National Rights.
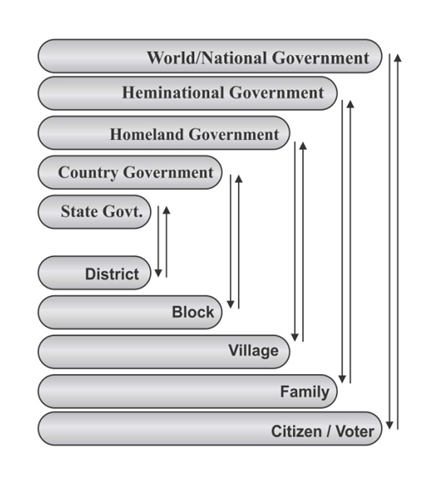
Homeland: The common territory of all neighboring countries, who have formed an union like European Union are referred to as ‘Homeland’.
International Problems: The challenges related to funds of local bodies or villages/wards that are listed to be addressed by the collective endeavor of union of two or more government of neighboring countries are referred to as "International Problems or problems of villages/wards."
International rights of villages/wards: The rights of the villages or wards necessary to address the above said international problems, granted by the constitution of union of neighboring countries, and the same can be protected by the right of filing petitions in local bench of international court of the union is termed ‘International Rights of villages/wards’.
Nation: The interconnectedness and commonness in values, socio-political challenges, civilization, culture and laws of all countries of the world is referred to as ‘nation’. ‘National’ is referred to something related to interconnected world. ‘National problem’ and ‘national rights’ are referred to global problems and global rights, respectively.
3. Identification of Global Problems and Global Rights
A list of 21 Global Rights (see website- https://mgc.world/global-rights ) was identified and submitted to the heads of state of 192 countries on April 10, 2024 for legal sanction. Some of these rights include the right to life and liberty, the right to be free from export-driven issues such as poverty, malnutrition, illiteracy and unemployment, the right to protection from international corruption, the right to international marriage, right of each and every individual and family for getting opportunities of personality development and growth respectively, right of getting adequate share in the domestic income of union of countries to develop all villages and wards and the right of protection from environmental hazards and ecological imbalances. A worldwide political renaissance is required for the people of Earth to secure and protect their Global Rights through the establishment of global agencies, institutions, parliament and government.
4.- Diagnosing the Causes of Global Problems and Revising Political Thoughts
The root causes of global problems have been attributed to outdated and incomprehensive political concepts such as –
a. Nation
b. Citizenship
c. Democracy
d. Sovereignty
e. Separation of power
In increasingly globalised world, information technology has enabled a few companies to gather and control the information affecting the mandate and mind of billions of people, across different countries. The conventional concepts of nation, sovereignty, citizenship, democracy, separation of power have already become outdated. But these outdated concepts are still being taught in universities worldwide. The corrections and updates to these political theories are articulated in the books written by Mr. Vishwatma, particularly in ‘Reinventing Democracy’ and ‘Password of Public Policy and Politics’.
5. Upgrading the United Nations and Forming a South Asian Union
On February 17-18, during the international conference of the World Social Forum (WSF) in Kathmandu, discussions on global problems and global rights led to the passing of two resolutions. The first resolution calls for the upgrading of the United Nations Organization to a United National Government (similar to a world government, but not exactly the same) to prevent the then ongoing wars and avert future conflicts, including a potential third world war. The second resolution proposes the formation of a South Asian Union (analogous to the European Union, but not exactly same) to ensure regional peace and prosperity. These resolutions were sent to the heads of state of 192 countries, including India on April 10, 2024, for signing international treaties.
6. Formation of the International organization “Global Agreement on Participation and Peace (GAPP)”
Mission for Global Change (MGC) a social organization founded by Mr. Vishwatma. a contemporary political thinker was a participant of the international conference of the World Social Forum (WSF) held in Kathmandu. MGC has taken initiative to implement above said two resolutions.
In this regard a three days long national Conference was held in Lucknow from September 11-13, 2024, to formulate the strategy for ensuring global peace and participation. A resolution was passed to create a new international organization called the Global Agreement on Participation and Peace (GAPP) as part of the Mission for Global Change (MGC). In order to manage the conflicts, insure grant of global rights and systematic prevention of wars this organization will prioritize human interests over national interests in its working. This organization will facilitate the international treaties required for the upgrading of the UN to a United National Government (UNG) and the formation of the South Asian Union, other regional unions of neighboring countries and hemi-national bodies. In order to counteract the negative effects of centralized power, the GAPP has given control over most supranational legislative and governing bodies to most local entities; such as villages/wards, families and individuals.
A draft constitution of the above mentioned international organisation was evolved with main motive to create collective force of the people and civil society of the earth desirous for grant of global rights of people and International Rights of local bodies. The organization will encourage other social organizations to join, and Governments to sign and ratify the GAPP treaty. By securing support of the overwhelming number of people and various governments we hope to upgrade United Nations, UNO to UNG (United nation’s Government), so that it may be enabled to protect Global Rights of human beings and prevent wars, where required by use of coercive powers such as sanctions, boycott and as a last resort, by use of force.
7. International Conference of Mission for Global Change (MGC) on Global Rights
A two days long national Conference was held in New Delhi on October 24-25, 2024, to formulate the strategy for people's action to get the global rights granted. During the conference, it was resolved to establish Interim Parliaments as international legislative bodies for the GAPP’s international units. These bodies will discuss international and global problems and will make rules, pass resolutions and draft treaties to help governments of all countries to address international and global challenges. The same bodies will also make rules for GAPP’s those respective vertical executive branches which will be working at international and global level. The interim regional, and global parliament shall have right to revise, change and upgrade the existing GAPP constitution.
The GAPP constitution establishes separate houses for representatives from countries and their provinces, from representative thoughts and from people dedicated to international and global rights. The Interim Parliaments will continue their work until governments sign the necessary treaties, after which General Assemblies of International units of GAPP, parallel to the Interim Parliament, will continue to work for ensuring GAPP's mission underlined as the safety and security of people, and for the economic development of own locality, for one’s own family and for the personality development of each and every individual of earth.
8. Purpose of Forming the Interim Parliaments
The current global scenario represents a state of war emergency. The risk of war spreading on a global scale is imminent. Traditional methods of addressing conflicts have proven to be inadequate and have, therefore, been consistently disregarded by nation-states. The conventional approach of fostering people-to-people dialogue has not been tried sufficiently, and, thus it has appeared to have failed and, therefore, been ignored by governments.
As a result, the formation of an Interim Parliament at three international tiers represents an action initiated by civil society in self-defense, on behalf of the general public. This initiative aims to harness the energy and expertise of former Prime Ministers, Members of Parliament (MPs), Members of Legislative Assemblies (MLAs), ministers, and diplomats. These individuals often hesitate to engage with traditional non-governmental organisations (NGOs). However, they may be drawn to participate in a mission that instills trust through visible, direct economic benefits, and, the granting of International Rights.
Extraordinary measures, such as the establishment of an Interim Parliament and an Interim Government, are essential to inspire trust among the general public and influential leaders alike. Achieving the prevention of wars and securing International and Global Rights requires the involvement of governments or organisations with government-like authority.
Currently, no global sovereign structure/power exists where international demands can be effectively raised. Hence, the urgent need arises to create a global sovereign power. The formation of a transitional institutions, such as three-tier Interim Parliaments and an Interim Governments, is indispensable to lay the groundwork for establishing such global authority. This institution can serve as a powerful tool to draw the attention of nation-states towards the mission of International Rights and global peace.
The general public is likely to trust and cooperate with initiatives aimed at preventing wars, securing Global Rights, and providing personal economic benefits only if extraordinary steps, such as the creation of an Interim Parliament and Interim Government, are taken. Such objectives cannot be achieved under the ambit and purview of an NGO alone.
Social organisations are generally structured around a single leadership, which can marginalise others with leadership potential. This dynamics often leads to divisions within society, as the organisational structure and working culture of NGOs tend to create factions. As a result, unity among communities with mutual hostilities becomes difficult to achieve.
In contrast, the parliamentary system of working embraces a more inclusive approach, accommodating diverse and even opposing communities. An organisation operating with a parliamentary culture can therefore serve as a global platform, bringing together activists from all communities, regardless of their differences.
9. Three-Phase Plan for Composing International and Global Interim Parliaments to Promote International Political Reforms
Implementing political reforms in South Asia and globally requires the efforts of civil societies and public movements. To build trust in global political reforms among the public, it is essential to select well-known and respected individuals from fields such as law, politics, journalism, industry, and bureaucracy as the members of the Interim Parliaments in first phase. In the second phase, sincere, dedicated and experienced social and political activists may be chosen as Members of Interim Parliaments. In the third phase, members will be elected by an electoral college comprising self-declared international and global citizens from around the world, and from all countries of South Asian region or from respective regional union.
10. Strategy for polarization of majority for Global Reforms and prevention of concentration of power
Only a small portion of the global population recognizes and seeks solutions to international issues, leading many to view global reform efforts as impractical. Since global reform relies on public mandate, it’s essential to engage those who can think beyond traditional nationalism.
Traditional nationalists often hold to a self-destructive notion of sovereignty and may be unaware of the impacts of globalization and modern information technology. Those who support unions of neighboring countries, like a model similar to the European Union, should be valued for their role in fostering a federal global structure. This structure would help to distribute supranational powers among various vertical governing bodies and to prevent concentration of power in one global authority.
Respect should also be extended to advocate to mobilize the developing and underdeveloped countries against injustices by global superpowers. Without this recognition, these individual countries might align with traditional nationalists. The only condition for this respect is that while they may consider global reforms impractical, they should refrain from opposing the reforms.
11. Campaign to Enroll people of supra-national mindset, Ambassadors, High Commissioners, Heads of Nation States, and Political Parties of all countries to Promote Reforms
GAPP will launch a campaign to enroll people of supra-national mindset of whole world by online method. GAPP will work to enlist Ambassadors, High Commissioners, Heads of Nation States, and recognized political parties worldwide to support international political reforms. Additionally, the campaign will extend to grassroots organizations, including farmers’ associations, labor unions, trade unions, spiritual groups, human rights organizations, and smaller political parties. The people of supra-national mindset will be encouraged to contribute on regular basis by online method to empower financially the GAPP organization advocating for granting the international and global rights. Directors of commercial firms and companies will also be encouraged to contribute their corporate social responsibility (CSR) funds to promote GAPP’s peace initiatives, benefiting both the cause and the businesses through public goodwill among GAPP supporters.
12. Formation of Interim Governments for Implementing Resolutions passed from International and Global Parliaments
To implement the resolutions and rules passed by the International, hemi-national and Global Parliaments, certain international, hemi-national and global executive committees of the GAPP will be established by the provisions of constitution of GAPP. These bodies will function as interim governments on transitional basis until the respective country governments ratify the necessary treaties. There is a significant possibility that countries may only partially accept the reforms in first phase suggested by the GAPP. Therefore, the GAPP constitution outlines two components of executive committees to operate at the international and global levels: the Interim Government and the Executive Committee. Both components will consist of members from the respective Interim Parliament and respective General Assembly of GAPP.
13. Alternative to the United Nations
Renaissance of people for global rights combined with the collective influence of prominent members of Interim Parliament, will drive ruling parties worldwide toward either cooperating and enacting political reforms or yielding power to reformers of their own country. This international movement will either lead to treaty ratification by governments or inspire the public to replace the United Nations with GAPP which will actively work to form United National Government, UNG.